Detecting AI: How Good are You?

angel narcisse design editor
AI and Teen Emotional Health
angel narcisse design editor As AI tools like ChatGPT and Snapchat’s virtual assistant become a part of teens’ everyday lives, educators and mental health professionals raise concerns about its long-term effects on emotional well-being. Data shows that most teens believe that AI won’t negatively impact their mental health, according to a survey conducted by Education Week. With many students referring to it as a tool that can provide convenient answers without the pressure of a real conversation. A group of Thibodaux High School juniors shared a range of opinions on AI’s role in emotional support. While some found the “synthetic environment” of AI appealing, others pointed out its shortcomings. “It’ll reword the same thing, but it’s just surface-level answers,” says Claire Bolton, a junior at Thibodaux High School. “AI can’t have true empathy, and it can lead to potentially harmful or non-helpful advice, especially since chatbots aren’t trained to handle serious mental health issues.” Kim Thompson, LCSW Kim Thompson, a Thibodaux-based licensed clinical social worker, says AI could foster a “false sense of belonging,” misleading teens into thinking they’re building meaningful connections when they’re only engaging with algorithms. “AI can’t have true empathy, and it can lead to potentially harmful or non-helpful advice, especially since chatbots aren’t trained to handle serious mental health issues,” she says. Although Thompson acknowledges that AI has potential benefits by introducing users to tools like mindfulness and breathing exercises, it could complement human-led support. But she says it’s all about balance, recommending that teens “use it cautiously and in tandem with professional support.” AI on the brain AI effects on teen mental health High School Students AI Impact on mental health over the next decade Educators AI Impact on mental health over the next decade EdWeek Research Center survey, 2024 Educator responses from a January 2024 survey of teachers, school leaders, and district leaders. The chart for students shows responses to a March 2024 survey of high school students
AI Pervasive In Everyday Life

lance jones staff People engage with AI in their daily routines, from online banking to classroom lessons — unknowingly benefiting from its efficiency and speed like simple text message correction, navigation assistance, or personalized customer service. “It’s really impressive how AI can offer suggestions, correct our grammar, or even choose an emoji that fits our mood without us thinking twice,” says Michelle Caruso, Vice President of Student Affairs at Nicholls. “I use Google Maps to navigate my way to work every day and I never really thought about it being AI, but it’s literally guiding me to the most efficient route using real-time data.” “I use Google Maps to navigate my way to work every day and I never really thought about it being AI, but it’s literally guiding me to the most efficient route using real-time data.” Michelle Caruso, Vice President of Student Affairs at Nicholls Charleston Rainey Jr., a safety management major at Nicholls, says AI enhanced customer service when he experienced a fraud incident with his online banking. “Instead of waiting hours for a human representative I was able to get the next steps within minutes,” says Rainey Jr. “The bot escalated the issue and set up an in-person visit rather than going through all the steps on the phone. It really sped up the process.” Rainey Jr. says the shift from human to AI-driven service is a growing trend in the banking sector, where AI handles initial inquiries and directs customers to the appropriate channels, saving time and reducing frustration. Jaiden Valure, a secondary education student at Nicholls, says that many teachers now use AI tools to help with curriculum development. “AI can offer lesson ideas, multiple teaching pathways, and suggestions that a teacher may not have thought of,” Valure says. Tools like ChatGPT assist educators in creating more engaging, diverse lesson plans, allowing them to focus on individualized student support. Valure pointed out that AI should remain a tool, not a substitute for human effort. “AI is great for helping with planning or understanding content, but it shouldn’t replace the human element in education,” Valure says. Rainy Jr. says while AI has many benefits, there is still a generational divide in its adoption. Younger people have grown up with technology and are more likely to embrace AI. However, older generations may struggle with the transition, especially when it comes to replacing face-to-face interactions with digital assistance. “It’s a challenge at first, but once they experience how quickly things get done, they’ll see the value,” Rainey Jr. says. “Older adults may initially be frustrated by the shift, but once they see the efficiency and convenience of AI, they will become more accepting.” ai tools by the numbers Top 10 AI Tools by Monthly Traffic Based on traffic volume from August 2024. Number rounded to the nearest million Data from Semrush and Similarweb, two reliable keyword research and web analytics platforms. AI Tools by Popular Task from AIxploria Image Generators MidJourney V6.1 Adobe Firefly 3 Stable Diffusion 3.5 Leonardo Ai FLUX.1 Ideogram 2.0 Recraft V3 Freepik DALL·E 3 Krea.ai Image Generators MidJourney V6.1 Adobe Firefly 3 Stable Diffusion 3.5 Leonardo Ai FLUX.1 Ideogram 2.0 Recraft V3 Freepik DALL·E 3 Krea.ai Writing & Web SEO Rytr QuillBot Undetectable AI ContentShake AI WriteSonic Free AI Content Writer Jasper GPTZero Paraphrasing Tool LanguageTool AI Chat & Assistant ChatGPT Claude AI Gemini AI Microsoft Copilot Grok by xAI Poe Meta AI ChatSonic Le Chat by Mistral AI Pi AI Education/Studies Perplexity AI Globe Explorer AI Poe QuillBot ChatPDF Notion AI FireFlies Deepl Coursera QuizLet AI Detection PimEyes Undetectable AI FaceCheck ID GPTZero Originality AI ZeroGPT Copyleaks Lenso.ai StealthGPT GeoSpy.ai Life Assistants Microsoft Copilot BeforeSunset AI AI HairStyles Roast Dating Ask Layla Tattoos AI Shop.app Recipes by AI Rewind AI Tripplanner AI Research & Science Perplexity AI WolframAlpha Consensus Scite.ai Liner AI Semantic Scholar Jenny AI Human or AI Tree of Knowledge AI SciSpace AI Writer The Future 5 AI about to hit the market and the latest advances Sora by Open AI a model capable of generating 60-second videos from simple text prompts Meta Movie Gen a powerful model for generating high-quality sound videos. Emote Portrait Alive give an image of a character to generate a video where the character speaks Adobe Firefly Video a model for video creation and editing. See full, current list
Detecting AI
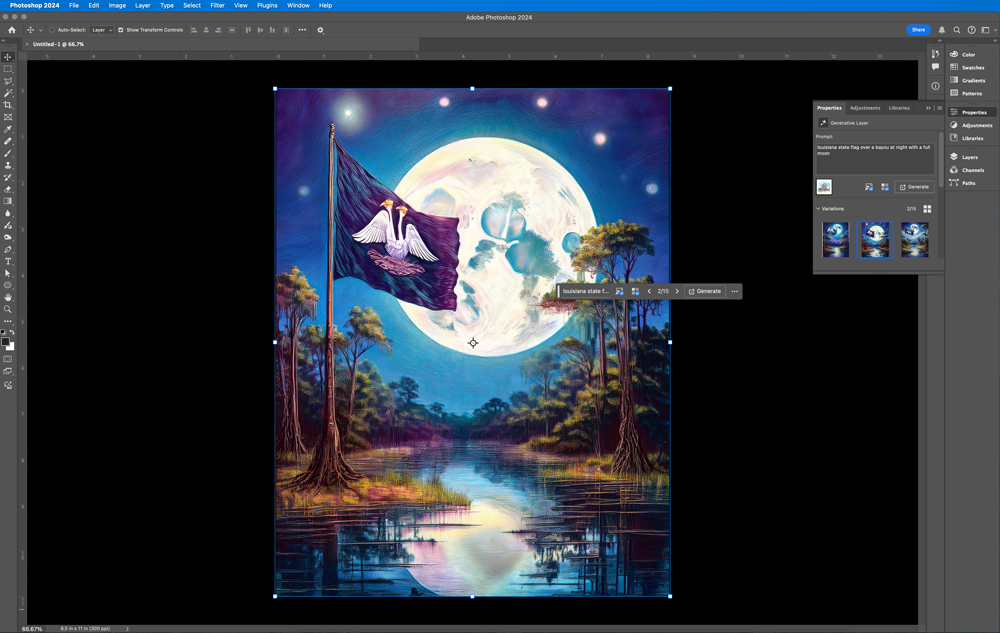
philip landry staff As Artificial Intelligence becomes more a part of our digital lives, more questions arise about its role in media and how to accurately detect it. While AI can enhance user experiences, distinguishing between human and AI-created content is increasingly vital. AI tools help businesses, influencers, and brands save time by producing posts, comments, and even images at scale. AI is used to keep content flowing, tailor posts for audiences, and can even spread misinformation. As AI grows more accessible, so does the challenge of identifying its presence online. According to the BBC, the best ways for someone to detect and identify AI in media is to pay attention to details, or to do a reverse image search. Similarly, an article put out by the Sante Fe Community College says to look for distorted imagery and watermarks, or to read the comments as AI can sometimes mimic human interaction to farm views, but it isn’t perfect. The most direct way to identify AI as well as misinformation in the media may be just thinking and observing for oneself. “We’ve always had people who manipulate the story to serve their agenda,” says Dr. Linda Martin, assistant professor of mass communication, “So maybe just old fashioned critical thinking or having a discerning eye… Knowing what good writing is.” “…just old fashioned critical thinking or having a discerning eye and knowing what good writing is.” linda martin, assistant professor of mass communication AI influence isn’t limited to social media. Customer service and video content are increasingly AI driven. Many companies are using chatbots to field customer questions, and often rely on pre-set answers, which is why some responses feel automated. In the film industry AI is powering Deep Fakes technology mostly used to alleviate costs in using computer graphics to change the way an actor looks. “Deep Fake AI use in movies is now being used to have a character age or be younger and it’s the same person,” says Melissa Remark, assistant professor of English, “In the past the CGI would have been really expensive and with Deep Fake AI technology it’s speeding that up.” As AI becomes more integrated into social media and our daily lives developing an eye for what’s real versus artificial is essential. Recognizing the patterns of AI-generated content and using verification tools can make it easier to identify content made with AI and understand a changing digital environment. AI image generated in Photoshop from the prompt, “louisiana state flag over a bayou at night with a full moon.” Student at Nicholls State University using AI on social media. Sophomore chemistry major Dylan Biffle uses AI to edit audio in the KNSU radio editing lab.
